Introduction
The Electric Vehicle (EV) has seen a resurgence in popularity in recent years, marking a significant shift in the automotive industry. While the concept of electric cars isn’t new – in fact, some of the earliest automobiles were electric – the Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) eventually dominated the market due to the abundance of fossil fuels and technological advancements.
Today, with growing concerns about climate change and air pollution, electric vehicles are poised to revolutionize transportation. This article will delve into the key factors driving the EV revolution, comparing electric cars with their gasoline-powered counterparts, and exploring the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.

How Electric Vehicles Work
Electric vehicles (EVs) operate on a fundamentally different principle than traditional gasoline-powered cars. Instead of relying on a combustion engine to generate power, EVs use a battery and an electric motor.
- Battery: The heart of an EV is its battery, which stores electrical energy. Batteries are typically made up of cells that contain a cathode, anode, and electrolyte. The type of battery used in EVs can vary, with lithium-ion batteries being the most common due to their high energy density and long cycle life.
- Electric Motor: The electric motor converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle. Electric motors are highly efficient and produce minimal noise and vibrations compared to internal combustion engines.
Charging System: EVs can be charged using various methods, including:
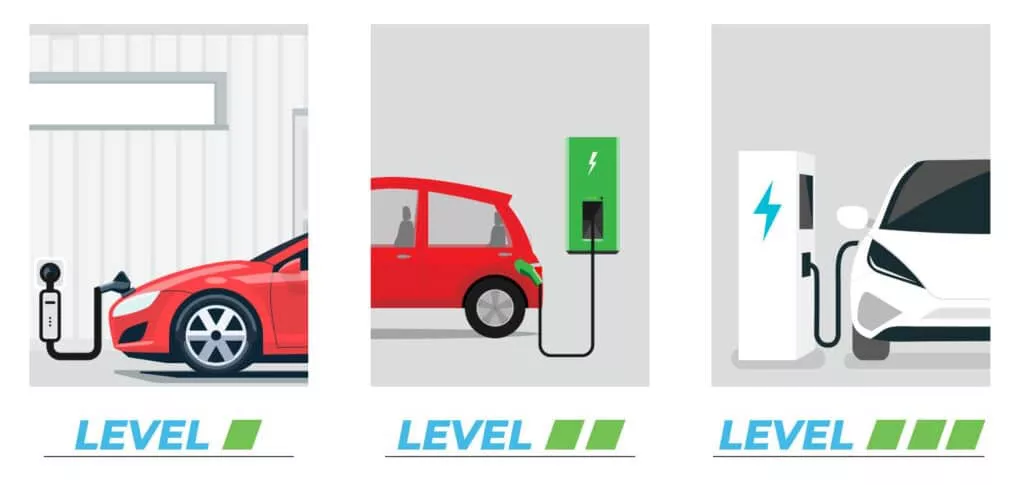
- Level 1 charging: Using a standard household outlet (slowest method)
- Level 2 charging: Using a dedicated charging station (faster than Level 1)
- DC fast charging: Using a high-power DC charger (fastest method)
Comparing Electric and Gasoline Vehicles
While electric vehicles have made significant strides, they still differ from traditional gasoline-powered cars in several key areas:
| Feature | Electric Vehicle | Gasoline Vehicle |
| Emissions | Zero tailpipe emissions | Significant greenhouse gas emissions |
| Fuel Economy | Energy efficient (electricity) | Dependent on fuel efficiency standards |
| Performance | Instant torque, quiet operation | Varies based on engine size |
| Maintenance | Fewer moving parts, lower maintenance costs | More frequent maintenance required |
| Purchase Price | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Operating Costs | Lower operating costs over time | Higher operating costs over time |
Environmental Benefits
One of the most significant advantages of electric vehicles is their positive impact on the environment:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas pollution.
- Improved Air Quality: EVs reduce the emission of harmful air pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM), leading to improved public health.
- Circular Economy: Advancements in battery recycling technology are making it possible to recover valuable materials from EV batteries, reducing waste and minimizing the environmental impact of battery production.
Challenges and the Future
Despite their numerous benefits, electric vehicles still face several challenges:

- Range Anxiety: The limited range of early EVs was a major concern. Advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure have helped alleviate this.
- Infrastructure Development: The availability of charging stations, especially in public areas and along major travel routes, is crucial for EV adoption. For now, many countries utilize their transportation routes with Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE).
- Cost: While battery costs have been declining, the initial purchase price of EVs can still be higher than gasoline-powered cars.
The future of electric vehicles is promising, with advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and government policies driving their adoption. As the costs continue to decrease and the benefits become more apparent, electric vehicles are poised to play a major role in shaping a cleaner and more sustainable transportation future.
References:

