A dead car battery can be an unexpected inconvenience, leaving you stranded at the most inopportune moments. While jump-starting a vehicle is a common solution, it is not always recommended due to potential safety risks and long-term battery damage.
According to the SAE J1494 standard, jump-starting is not officially advised as it can cause electrical system failures, battery damage, and, in some cases, personal injury.
Preventative maintenance and the use of a high-quality battery charger are always recommended to extend the lifespan of a vehicle’s battery. If a jump-start becomes necessary, it is essential to follow the correct procedure to minimise risks.
- Essential Items for a Safe Jump-Start
- Step-by-Step Guide to Jump-Starting a Vehicle
- Step 1: Position the Vehicles Correctly
- Step 2: Identify the Battery Terminals
- Step 3: Connect the Jumper Cables in the Correct Sequence
- Step 4: Start the Assisting Vehicle
- Step 5: Start the Vehicle with the Dead Battery
- Step 6: Safely Disconnect the Jumper Cables (Reverse Order)
- Step 7: Allow the Battery to Recharge
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Jump-Starting a Car
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- References
Essential Items for a Safe Jump-Start
Before beginning the jump-starting process, ensure you have the following items:
- Jumper cables – In good condition, with no visible wear or damage.
- A functioning vehicle – A car with a charged battery to assist the dead one.
- Protective gloves & safety glasses – Recommended for personal safety.
- Battery cleaning materials – A clean cloth or brush to remove corrosion from terminals.
Tip: If battery terminals are corroded, a mixture of baking soda and water can be used to clean them, ensuring a secure connection for the jumper cables.
Step-by-Step Guide to Jump-Starting a Vehicle
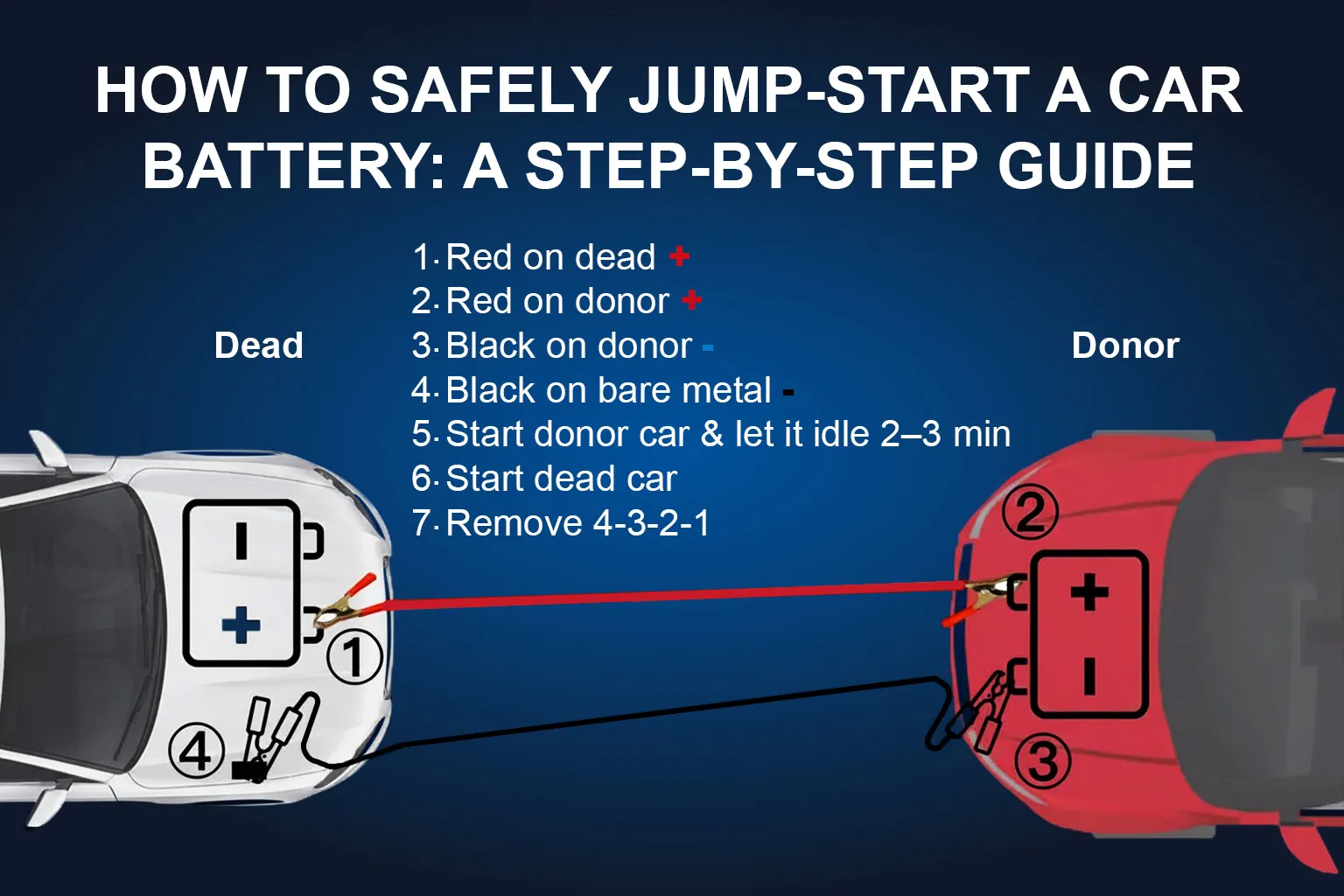
Step 1: Position the Vehicles Correctly
- Park the assisting vehicle close enough so that the jumper cables can reach both batteries but without the vehicles touching.
- Turn both vehicles off and engage their parking brakes.
- Open the hoods and locate the battery terminals.
Step 2: Identify the Battery Terminals
- Find the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals on both batteries.
- Ensure the terminals are clean before proceeding.
Step 3: Connect the Jumper Cables in the Correct Sequence
It is crucial to follow the correct order to prevent electrical damage or injury.
- Attach one red clamp to the positive (+) terminal of the dead battery.
- Attach the other red clamp to the positive (+) terminal of the assisting battery.
- Attach one black clamp to the negative (-) terminal of the assisting battery.
- DO NOT connect the remaining black clamp to the dead battery’s negative terminal. Instead, attach it to an unpainted metal surface on the engine block or chassis of the dead car.
Reason: This reduces the risk of sparks, which could ignite flammable gases around the battery.
Step 4: Start the Assisting Vehicle
- Turn on the assisting vehicle and allow it to run for at least 2–3 minutes to transfer power to the dead battery.
Step 5: Start the Vehicle with the Dead Battery
- Attempt to start the car. If it does not start immediately, wait a minute and try again.
- If the vehicle does not start after multiple attempts, the battery may no longer be capable of holding a charge.
How the Jump-Start Works:
- The assisting vehicle’s battery supplies enough power to start the dead vehicle.
- Once the dead vehicle starts, its alternator will take over to keep the engine running.
Step 6: Safely Disconnect the Jumper Cables (Reverse Order)
- Remove the black clamp from the metal surface of the dead car.
- Remove the black clamp from the assisting battery.
- Remove the red clamp from the assisting battery.
- Remove the red clamp from the previously dead battery.
Ensure the clamps do not touch each other while still connected, as this could cause an electrical short.
Step 7: Allow the Battery to Recharge
- Keep the jump-started vehicle running for at least 15–30 minutes to allow the alternator to recharge the battery.
- Driving the vehicle is preferable to idling, as it charges the battery more effectively.
💡 Tip: If the battery dies again soon after, it may no longer hold a charge and should be replaced.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Jump-Starting a Car
Best Practices
✔ Always ensure correct terminal connections before jump-starting.
✔ Conduct the procedure in an open, well-ventilated area to avoid exposure to battery fumes.
✔ Use properly insulated jumper cables to prevent electrical hazards.
Avoid These Mistakes
✖ Do not allow metal clamps to touch while connected—this can cause sparks.
✖ Never attempt to jump-start a leaking, swollen, or damaged battery—it should be replaced immediately.
✖ Avoid jump-starting near flammable substances such as petrol or oil.
What If Jump-Starting Does Not Work?
If a jump-start does not resolve the issue, the problem may not be the battery. Other potential causes include:
- Battery is too old – Most vehicle batteries last 3–5 years before requiring replacement.
- Loose or corroded battery terminals – Poor connections can prevent proper power transfer.
- Faulty alternator – If the alternator is not functioning, the battery will not remain charged.
- Defective starter motor – If the starter is failing, the engine will not crank, even with a fully charged battery.
If these issues persist, it is recommended to visit a professional service centre for a thorough diagnostic check.
Alternative Solutions to Jump-Starting
✔ Use a battery charger – A slow charge is safer and extends battery life.
✔ Call roadside assistance – Professional technicians can diagnose the exact issue.
✔ Replace the battery – If the battery frequently dies, it may need replacement.
Final Recommendation: Use Jump-Starting Only as a Last Resort
While jump-starting can provide a temporary solution, it is not always advisable. The SAE J1494 standard cautions against routine jump-starting due to the potential risks to a vehicle’s electrical system and overall battery health.
At Suzuki, we always recommend preventative maintenance and using a high-quality battery charger whenever possible to extend battery life and avoid sudden failures. If a battery frequently loses charge, replacing it is the safest long-term solution.
Find High-Quality Batteries & Professional Service
For optimal performance and reliability, choose a high-quality battery from a trusted supplier. Visit a professional service centre for expert battery checks and replacement services.
Conclusion
Choosing the right car battery is essential for reliable starts and long-term vehicle performance. By focusing on key factors such as specifications, battery type, CCA, RC, warranty, and driving conditions, you ensure durability and peace of mind. Opting for maintenance-free designs and trusted brands provides added convenience, while professional installation and recycling support both safety and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
References
- Society of Automotive Engineers. (2012). Battery Booster Cables. SAE International.
- Erjavec, J., & Thompson, R. (2016). Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (7th ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Bosch Automotive Handbook (10th ed.). (2018). Wiley.
- Linden, D., & Reddy, T. B. (Eds.). (2002). Handbook of Batteries (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
- Crouse, W., & Anglin, D. (2012). Automotive Mechanics (10th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.

