Introduction
Selecting the right battery is critical for powering everything from cars to solar systems. Flat plate and tubular plate batteries, two common lead–acid battery designs, differ significantly in structure, performance, and application. Understanding these differences empowers consumers, technicians, and engineers to make informed decisions that optimise efficiency, longevity, and cost. This article breaks down the technical distinctions, benefits, and ideal use cases of each battery type to guide your choice.
What Are Flat Plate and Tubular Plate Batteries?
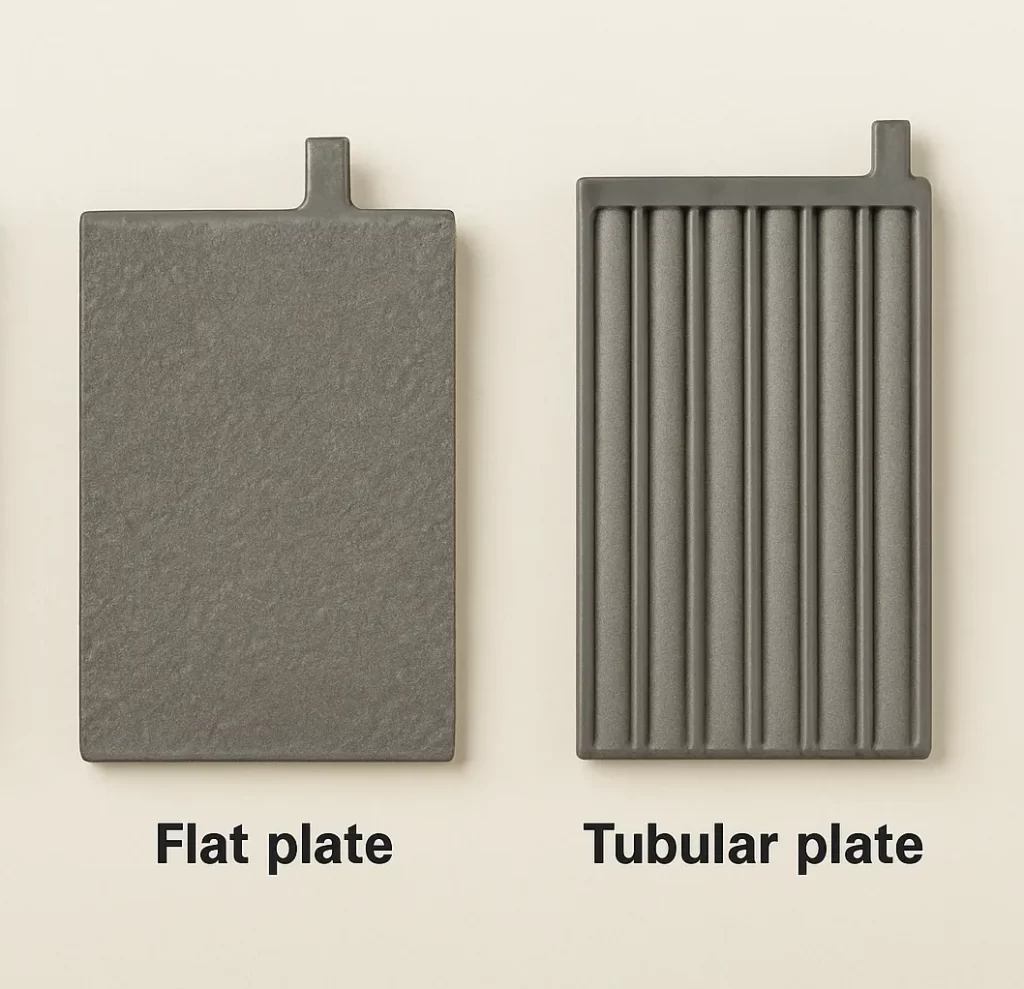
Flat Plate Batteries
Flat plate batteries feature thin, flat lead alloy grids coated with active materials (e.g., lead dioxide and sponge lead). Their design maximises electrolyte contact for rapid chemical reactions, making them ideal for delivering quick bursts of energy in applications such as automotive starting or backup power.
Key Features:
- Compact and cost-effective
- Suited for shallow cycling
- Lower production costs
Tubular Plate Batteries
Tubular plate batteries use lead spines encased in porous tubular sleeves to hold active material. This design minimises material shedding and corrosion, extending lifespan and enhancing deep-cycle performance. They excel in renewable energy systems and heavy-duty industrial applications.
Key Features:
- Exceptional longevity
- Optimised for deep cycling
- Higher initial cost but highly durable
Technical Comparison
| Feature | Flat Plate Battery | Tubular Plate Battery |
| Design | Flat grid with pasted active material | Cylindrical spines in porous tubes |
| Cycle Life | Moderate (~500–800 cycles) | Long (~1,200–1,500 cycles) |
| Deep Discharge | Limited performance | Superior performance |
| Maintenance | Low (sealed versions) | May require water topping (flooded types) |
| Applications | Cars, UPS, emergency lighting | Solar, inverters, forklifts, telecom |
| Energy Density | High for short bursts | Steady for prolonged use |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Higher upfront, lower long-term cost |
Performance Insights
- Flat Plate Batteries: Their large surface area supports rapid charge–discharge cycles, ideal for automotive starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) systems. However, frequent deep discharges can cause active material shedding, reducing lifespan (typically 3–5 years). Best for budget-conscious users needing reliable, low-maintenance power for light use.
- Tubular Plate Batteries: Engineered for endurance, their tubular design retains active material better, ensuring stability during deep discharges. They offer 50–80% longer life than flat plate batteries in deep-cycle applications (e.g., solar storage) and handle temperature fluctuations better, making them ideal for outdoor or demanding environments.
Pros and Cons
Flat Plate Batteries
Pros:
- Affordable and widely available
- Lightweight and easy to install
- Minimal maintenance (especially sealed models)
Cons:
- Shorter lifespan under heavy use
- Not suited for frequent deep cycling
- Prone to material degradation over time
Tubular Plate Batteries
Pros:
- Superior deep-cycle performance
- Extended lifespan (5–8 years or more)
- Reliable in harsh conditions
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost
- Heavier and bulkier design
- Flooded versions may need periodic maintenance
Applications
- Flat Plate Batteries:
- Automotive SLI systems (cars, trucks)
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) for homes/offices
- Emergency lighting and backup systems
- Tubular Plate Batteries:
- Renewable energy storage (solar, wind)
- Industrial equipment (forklifts, traction systems)
- Telecom and remote power solutions

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Conclusion
Choosing between flat plate and tubular plate batteries depends on your needs. Flat plate batteries offer affordability and simplicity for light, short-term use, such as in cars or backup systems. Tubular plate batteries, with their superior durability and deep-cycle performance, are the go-to choice for solar, industrial, or heavy-duty applications. By understanding these differences, you can select a battery that balances cost, performance, and longevity for your specific use case.
References
- Crompton, T. (2000). Lead–acid secondary batteries. In Battery Reference Book (3rd ed., pp. 1–11). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-075064625-3/50004-4
- Wagner, R. (2017). Positive active-materials for lead–acid battery plates. In Lead–Acid Batteries: Science and Technology (pp. 235–267). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63700-0.00008-8
- Ferg, E., Loyson, P., & Poorun, A. (2006). The addition of red lead to flat plate and tubular valve regulated miners cap lamp lead–acid batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 155, 428–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.04.029
- Guo, Y., Wu, T., & Zhang, M. (2005). Current and potential distributions of large-sized positive plate in its formation of lead–acid batteries. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 152(2), A415–A420. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1851034
- Terzaghi, G. (1998). Engineered woven gauntlets to improve the performance of lead/acid tubular plates. Journal of Power Sources, 73(1), 78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(98)00024-X

