Battery
One or more electrochemical cells which electrically coupled into a single unit and equipped with external electrical connections’ attachments. In a lead-acid battery, the cell has an open-circuit voltage of approximately 2.1 volts. Six cells are linked together to make a 12-volt lead-acid battery.
How does Battery operate?
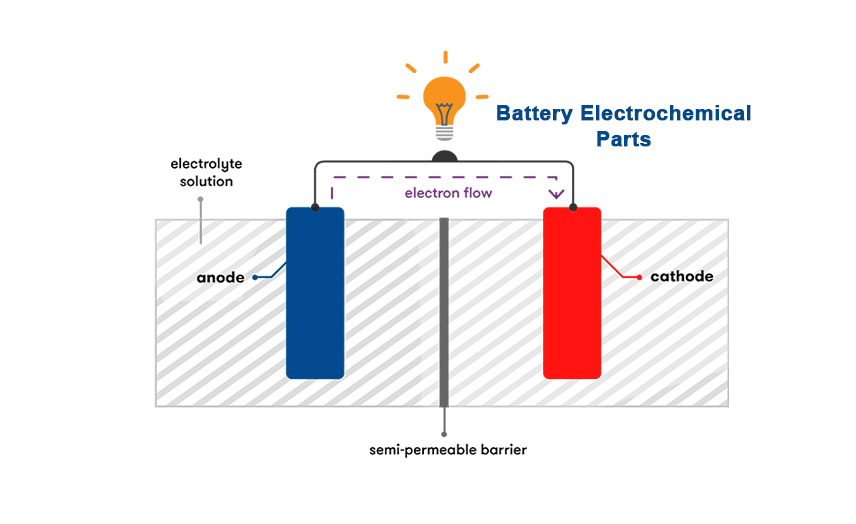
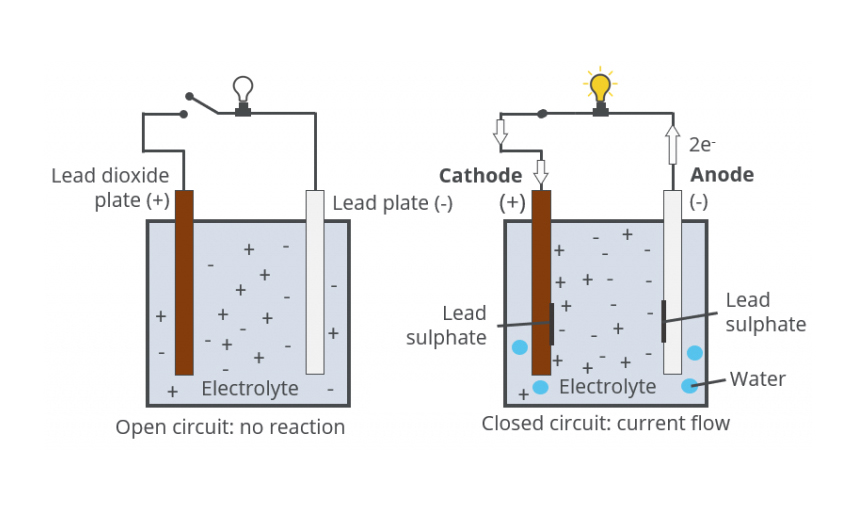
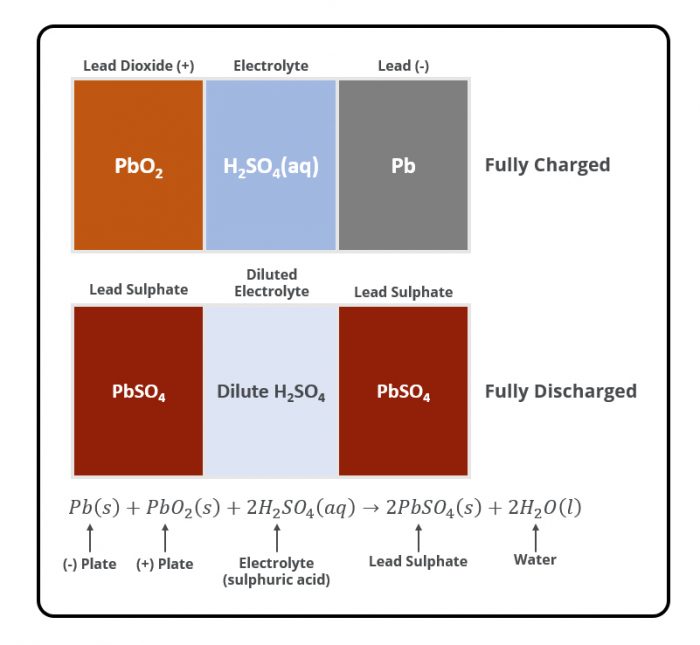
When two unlike materials such as the positive and negative plates are immersed in Sulphuric acid (electrolyte), a battery is created and voltage is developed. The voltage developed depends on the types of materials used in the plates and the electrolyte used. In a Lead-Acid battery, the voltage developed is approximately 2.1 volts per cell. Electrical energy is produced by the chemical reaction between the different materials and the electrolyte. When the chemical reaction begins, electrical energy flows from the battery as soon as there is a circuit between the positive and negative terminals. The electrical current flows as electrons through the outside circuit and as charged ions between the plates inside the battery.
Starter battery
Battery which designed to provide a large flow of current for a short period of time. This wave of current turns the engine on during the starting process. The burst of energy only discharges few percentages of the battery which will be recharged again by the alternator. Under normal use, a car battery may go through its entire life without ever being discharged more than 20 % of its total capacity.
Various Technologies in Starter Batteries

ISO and IEC maintain terminological databases for use in standardization at the following addresses:
- Flooded battery (SLI flooded lead-acid battery) having a cover provided with one or more openings through which gaseous products may escape.
- Enhanced flooded battery (EFB flooded lead-acid battery) with additional special design features to significantly improve the cycling capability compared to standard flooded batteries.
- Valve regulated lead-acid battery (VRLA lead-acid battery) which is closed under normal conditions but which has an arrangement that allows the escape of gas if the internal pressure exceeds a predetermined value Note 1 to entry: The VRLA battery cannot receive addition to the electrolyte and after activation of dry-charged VRLA. Note 2 to entry: In VRLA batteries the electrolyte is immobilized.
- Absorbent glass mat battery (AGM battery) is VRLA battery in which the electrolyte is immobilized by absorption in a glass mat.
- Gel battery (Gel VRLA battery) in which the electrolyte is immobilized by fixing as a gel.

 العربية
العربية Русский
Русский
Is the performance of car batteries and other batteries always the same or are new technologies also used in batteries?
Car battery technology is different from other batteries and is becoming more advanced every day.